“This article was published on 2021/12/29. The Euler v2 has already launched on 2024 Feb. Readers are advised to take note and understand.”
 In 2020, before the DeFi Summer initiated the craze for Decentralized Finance (DeFi), DeFi applications primarily focused on lending protocols. This included prominent projects like Maker and Compound, which were based on mainstream tokens and stablecoin lending protocols, along with emerging platforms like Aave and Curve. However, listing a token on a lending protocol required a permissioned listing mechanism to reduce user asset risks. The development team at Euler XYZ introduced the permissionless lending protocol Euler, allowing tokens with trading pairs on Uniswap V3 to be listed on the lending market. Through a series of mechanisms, Euler enhances liquidity and reduces risks. Euler was launched on the mainnet on December 13, 2021. This article is based on the official whitepaper and aims to introduce the operation of the new open lending protocol Euler.
In 2020, before the DeFi Summer initiated the craze for Decentralized Finance (DeFi), DeFi applications primarily focused on lending protocols. This included prominent projects like Maker and Compound, which were based on mainstream tokens and stablecoin lending protocols, along with emerging platforms like Aave and Curve. However, listing a token on a lending protocol required a permissioned listing mechanism to reduce user asset risks. The development team at Euler XYZ introduced the permissionless lending protocol Euler, allowing tokens with trading pairs on Uniswap V3 to be listed on the lending market. Through a series of mechanisms, Euler enhances liquidity and reduces risks. Euler was launched on the mainnet on December 13, 2021. This article is based on the official whitepaper and aims to introduce the operation of the new open lending protocol Euler.
Team Overview
Euler Finance is an permissionless lending protocol developed by the Euler XYZ team, founded by three individuals. The CEO, Michael Bentley, previously served as an evolutionary biologist at the University of Oxford. The other two co-founders are Doug Hoyte and Jack Prior, who are also developers at Euler XYZ. Additionally, Mick de Graaf, an advisor to the team, is a co-founder of DEFIED.io, a decentralized asset management platform on the Ethereum chain, and previously served as the Chief Developer at PieDAO, an on-chain index fund. In August 2021, Euler secured an $8 million Series A funding round led by Paradigm, with other investors including Lemniscap and individual investors from well-known blockchain projects such as The Daily Gwei, Bankless, Synthetix, Coinbase, and Product Hunt.
Six innovative featrues
Euler Finance has six unique features compared to traditional DeFi lending protocols, which are introduced below to help readers better understand Euler Finance.

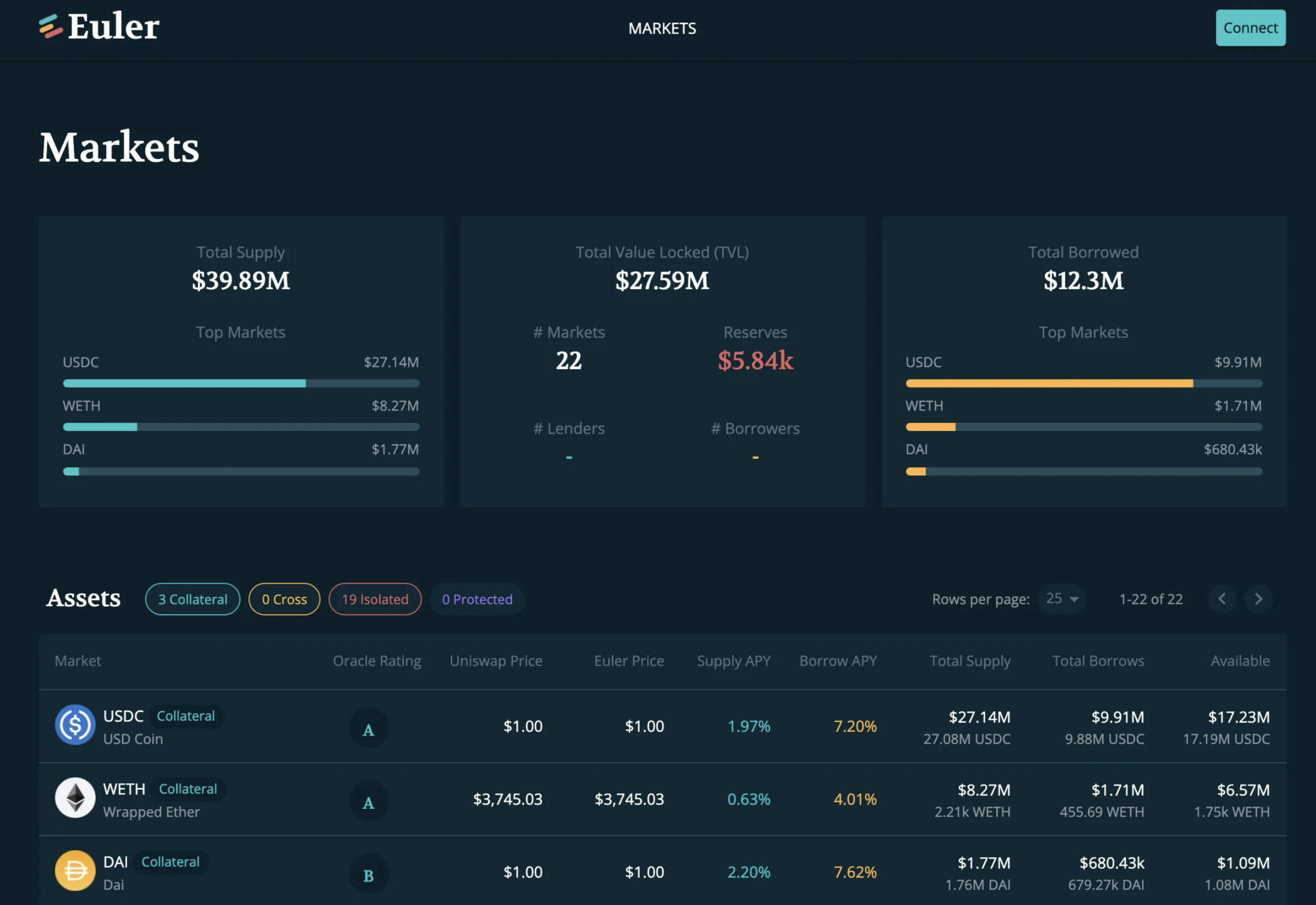
Permissionless listing
Euler Protocol allows users to decide which assets can be listed on the lending protocol, and users can add any assets that have WETH trading pairs on Uniswap v3 to Euler Finance. Through the multi-tier asset classification mechanism, Euler Finance reduces user asset risk.
Asset tiers
Although Euler Finance allows users to add assets to the lending protocol, it poses a significant system risk. Therefore, Euler Finance introduces a multi-tier asset classification design, where assets are classified based on risk, to protect Euler Finance protocol and users.
- Isolation Tier Assets: Isolation tier assets can be used for general lending, but cannot be used as collateral to borrow other assets. Isolation tier assets cannot be used with other assets in the same collateral pool for lending. For example, if a user holds $USDC and $DAI as collateral and wants to borrow isolation tier asset $ABC, they can only borrow $ABC. If they want to borrow another asset $XYZ later, they need to use another Euler Finance account to operate.
- Cross Tier Assets: Cross tier assets can be used for general lending, but cannot be used as collateral to borrow other assets. However, cross tier assets can be used with other assets for borrowing. For example, if a user holds $USDC and $DAI as collateral and wants to borrow cross tier assets $ABC and $XYZ, they can use the same Euler Finance account to operate.
- Collateral Tier Assets: Collateral tier assets can be used for general lending and cross-lending, and can also be used as collateral. For example, if a user deposits collateral tier assets $USDC and $DAI, they can use them to borrow collateral tier assets $UNI and $LINK, and use the same Euler Finance account to operate.
Euler Finance’s native governance token $EUL holders can vote to release assets from isolation tier and promote them to cross tier or collateral tier through the governance mechanism. This helps to improve Euler Finance’s capital efficiency, but also exposes users to greater risk. Balancing these factors will help maximize $EUL holders’ interests.
Reactive interest rates
In Compound and Aave, interest rates are set using static linear (or segmented linear) interest rate models to affect the cost of borrowing in the lending protocol. In general, when the demand for borrowing increases or the supply of funds decreases, interest rates rise; when the supply of funds increases or the demand for borrowing decreases, interest rates fall. While a static model can work well if the parameters are correctly set, if the parameters are incorrect, it can lead to borrowing costs that are too high or too low.
To avoid the need to choose the correct parameters for each borrowing market, Euler uses a PID controller to amplify (dampen) interest rate changes when interest rates are above (below) the target utilization rate threshold. This produces responsive interest rates that adapt to the market situation of the target asset in real-time, without the need for continuous governance to intervene.
MEV-resistant liquidations
In Compound and Aave, asset liquidations are performed by discounting the collateral by a fixed percentage (usually 5-10%) and providing the borrower’s collateral to the liquidator as an incentive to liquidate. Potential liquidators often only have access to the liquidation reward through the “Priority Gas Auction” (PGA) mechanism, which exposes the liquidation reward to what is known as Miner Extractable Value (MEV). This mechanism is not friendly to large borrowers and does not incentivize small liquidations.
To address these issues, Euler does not use a fixed discount rate, but instead uses a Dutch auction and provides a discount acceleration mechanism for liquidity providers. Euler allows borrowers to adjust their risk after the value of their debt exceeds the value of their collateral, and liquidators can earn more discounts as the difference between the two increases. Additionally, Euler provides a discount acceleration mechanism (discount booster) for liquidity providers, allowing them to earn profits before miners and front-runners in the Dutch auction.
Protected collateral
In Compound and Aave, collateral deposited in lending protocols can always be borrowed. However, in the Euler protocol, collateral can be deposited but not used for borrowing. This type of collateral is termed “protected.” These protected collaterals do not earn interest for users but eliminate the risk of borrower default. Users can withdraw the collateral assets at any time, preventing borrowers from using tokens to influence governance decisions or take short positions
Multi-collateral stability pools
In other lending protocols, liquidation typically relies on external liquidity sources. However, this method faces challenges such as inaccurate pricing due to factors like slippage, swap fees, extreme volatility, price smoothing algorithms (e.g., TWAP on Euler), and delayed new price releases.
To address these issues, Euler allows lenders to support liquidation by providing liquidity to stability pools associated with each lending market. Liquidity providers in these pools earn interest by depositing eTokens while awaiting liquidation. This setup prevents manipulation attempts during the unstaking period and enables immediate internal liquidation when a borrower defaults. The liquidity from stability pools is used to cancel the borrower’s debt and return discounted collateral to the pool after deducting fees.
This approach extends the concept of stability pools pioneered by Liquidity protocols into a multi-collateral form on Euler. The primary advantage of using stability pools is the ability to handle liquidation promptly when a borrower defaults, without relying on external liquidity sources
Conclusion
The innovative features of Euler focus on the perspectives of both lenders, borrowers, and liquidators. Through mechanisms like permissionless listing, optimized liquidation processes, and responsive interest rates, Euler caters to the diverse needs of participants in the lending market. Additionally, by utilizing multi-collateral stability pools, lenders can ultimately passively convert all their eTokens into liquidation collateral assets
Although these innovative characteristics open new perspectives in the lending protocol domain, aspects such as the low liquidity of long-tail assets with $WETH pairs on Uniswap and the feasibility of Euler’s operational mechanism are still worth continued observation. Furthermore, Euler is set to launch its native governance token $EUL, which can be used for voting on asset levels, collateral ratios, borrowing rates, and other protocol parameters
Reference
- Euler Finance White Paper
- Euler|Series A Led by Paradigm
- CoinDesk|Euler Finance Launches New DeFi Lending Platform in Crowded Market